I-SceI BioVector®表达质粒expression plasmid-BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌株细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
- 价 格:¥49850
- 货 号:BioVector® I-SceI
- 产 地:北京
- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
I-SceI BioVector®表达质粒expression plasmid-BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌株细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
The BioVector® I-SceI expression plasmid is a genetic tool used in molecular biology for studying DNA repair mechanisms, particularly in the context of site-specific double-strand breaks (DSBs). The I-SceI endonuclease is a rare-cutting enzyme that recognizes and cleaves a specific 18-base pair DNA sequence (5'-AAGAGGAGGTAACAGGGTA-3'). The expression plasmid for I-SceI contains the gene encoding the I-SceI enzyme, which can be introduced into cells to induce double-strand breaks at the specific target sequence, allowing researchers to study how cells repair these breaks.
Key Features of I-SceI Expression Plasmids:
I-SceI Gene: The plasmid typically carries the gene that encodes the I-SceI endonuclease, which can be transfected into target cells. The gene is often driven by a strong promoter like the CMV promoter (Cytomegalovirus) for high expression in mammalian cells.
Double-Strand Break Induction: The enzyme makes a double-strand break at a specific DNA sequence, often inserted into the genome or a plasmid within the cells. This induced break can be used to study:
DNA repair pathways (like non-homologous end joining [NHEJ] and homologous recombination [HR]).
Genomic stability.
Mutagenesis or gene editing.
Applications:
Homologous recombination assays: The I-SceI expression plasmid can be used to create breaks in the genome to test how cells repair DNA through homologous recombination or NHEJ.
Gene targeting and editing: In conjunction with donor DNA, this system can be used for gene editing by inducing double-strand breaks at specific loci.
DNA repair studies: The repair of the double-strand break by the cell's repair mechanisms can be studied in terms of repair efficiency, error rates, and involvement of different repair pathways.
Mutagenesis: Inducing double-strand breaks allows for mutagenesis at specific locations in the genome, which can be useful in functional genomics.
Vectors: The plasmid carrying the I-SceI gene can come in various forms, such as a viral vector for efficient delivery into cells, or expression plasmids for transient expression. These vectors may also carry additional reporter genes (e.g., GFP or luciferase) to monitor the success of DNA repair or the cellular response to the break.
Experimental Approach:
Inducing DSBs: Transfecting the I-SceI expression plasmid into cells leads to the expression of the I-SceI endonuclease, which induces a double-strand break at the target site in the genome.
Repair Studies: After the break, cells attempt to repair the damage using endogenous repair mechanisms, which can be studied to assess the involvement of repair proteins or pathways, such as BRCA1/BRCA2 for homologous recombination or Ku70/80 for NHEJ.
Measuring Repair Outcomes: Researchers can measure repair efficiency by sequencing the repair junctions or using reporter assays, such as the green fluorescent protein (GFP) or luciferase expression.
Map
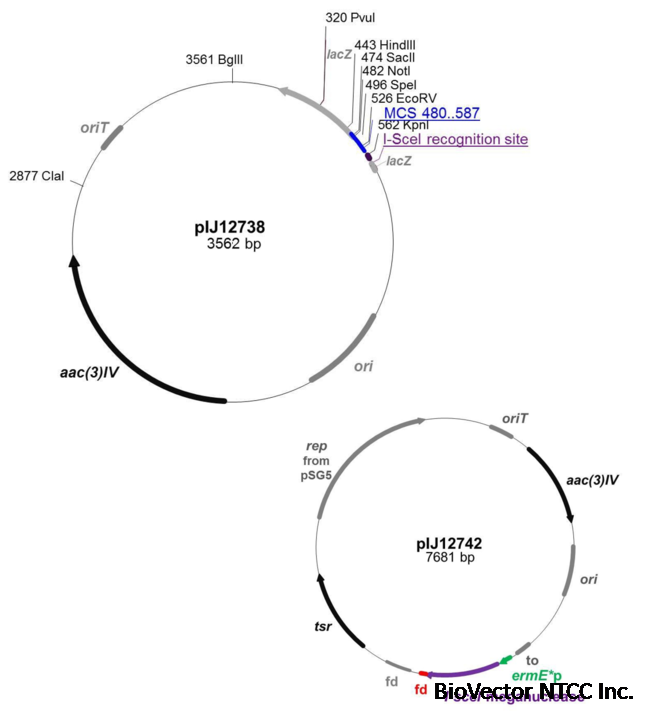

生产厂家Supplier:
BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌株细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
E-mail:BioVector@163.com
- 公告/新闻