pMTL-ME3 & pMTL-GL3,pMTL-YN3,pMTL-YN4,pMTL-JPB22梭菌基因敲除载体Clostridium Knock-out质粒-BioVector保藏中心
- 价 格:¥49850
- 货 号:BioVector®-PMTLKO1
- 产 地:北京
- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
pMTL-SC7215, pMTL-SC7315 & pMTL-SC7515,pMTL-KG146/147,pMTL-ME3 & pMTL-GL3,pMTL-YN3,pMTL-YN4,pMTL-JPB22梭菌基因敲除载体Knock-out质粒
BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌株细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
Clostridium Knock-Out Vectors
Knock-out vectors are available for the generation of mutants in a classic two-step process by allelic exchange [1], where either replication deficient (suicide) or defective (pseudo-suicide) vectors carrying appropriate mutant alleles integrate into the genome via homologous recombination, and the double crossover mutants arise by plasmid excision in which the wildtype allele has exchanged with the mutant allele formerly on the plasmid – allelic exchange.
The isolation from single crossover integrants of those cells that have lost the plasmid to form double crossover mutants is reliant on the use of the counter selection markers codA or pyrE [1]. They may only be used in cells that lack functional equivalents, either naturally occurring or deliberately created.
[1] codA-based plasmids (pMTL-SC7215, pMTL-SC7315 & pMTL-SC7515)
Based on the counter selection marker codA encoding cytosine deaminase which catalyzes the conversion of 5-fluorocytosine (FC) into the highly toxic 5-fluorouracil (FU). Plasmid SC7215 relies on the pBP1 replicon for the most effective pseudo-suicide in C. difficile R20291, SC7315 incorporates the pCB102 replicon for use in C. difficile 630 [2] and SC7315 is based on the pIM13 replicon for use in C. acetobutylicum [3].

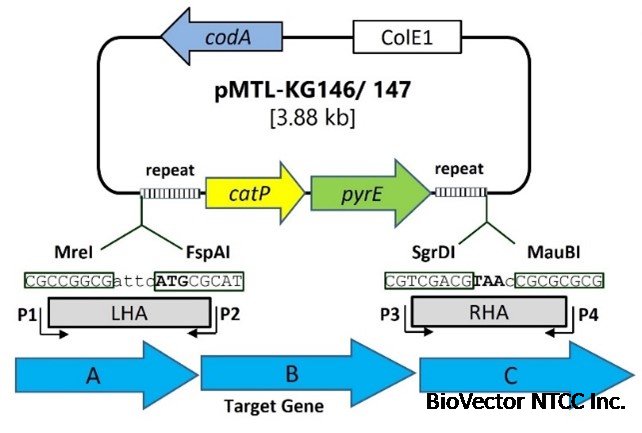
[2] codA– and pyrE-based plasmids (pMTL-KG146/147)
A suicide system for gene knock-out in C. acetobutylicum [4], relying on ColE1 for replication in E.coli and the catP for selection (chloramphenicol resistance). The counterselection marker is codA (selecting on 5-FC). The presence of pyrE and flanking repeat sequences, allows for the direct selection of clean, in-frame deletions by plating on FOA, and so the system can only be used in a pyrE deletion strain of C. acetobutylicum.
[3] pyrE-based plasmids
The pyrE gene encodes orotate phosphoribosyltransferase, an enzyme involved in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis and which renders cells sensitive to 5-fluoro-orotatic acid (FOA). Heterologous pyrE genes are employed in specific, uracil auxotrophs created by deleting the 3’-end of the native pyrE gene using Allele-Couple Exchange (ACE) [5].
pMTL-ME3 & pMTL-GL3
Based on the pIM13 replicon and a C. spororgenes pyrE gene, pMTL-ME3 was developed for the creation of mutants in C. acetobutylicum [3]. Plasmid pMTL-GL3 was derived from pMTL-ME3 through deletion of the pIM13 replicon and shown to function as a suicide system in C. beijerinckii [6].


pMTL-YN3 and pMTL-YN4
Based on the pCB102 replicon (pMTL-YN3) or the pBP1 replicon (pMTL-YN4) and a C. spororgenes pyrE gene, the two KO vectors were designed for use in C. difficile R20291 and in C. difficile 630, respectively [7].
pMTL-JPB22
A suicide system for gene-knockout strain production in A. woodii [8,9,10], relying on ColE1 for replication in E.coli and the catP for selection (chloramphenicol resistance). The counterselection marker is pyrE (selecting on FOA), and so the mutant can only be used in a pyrE deletion strain of A. woodi.

BioVector质粒载体菌株细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
电话:400-800-2947
Email:Biovector@163.com
企业QQ/微信:1843439339
网址http://www.biovector.net
- 公告/新闻