- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
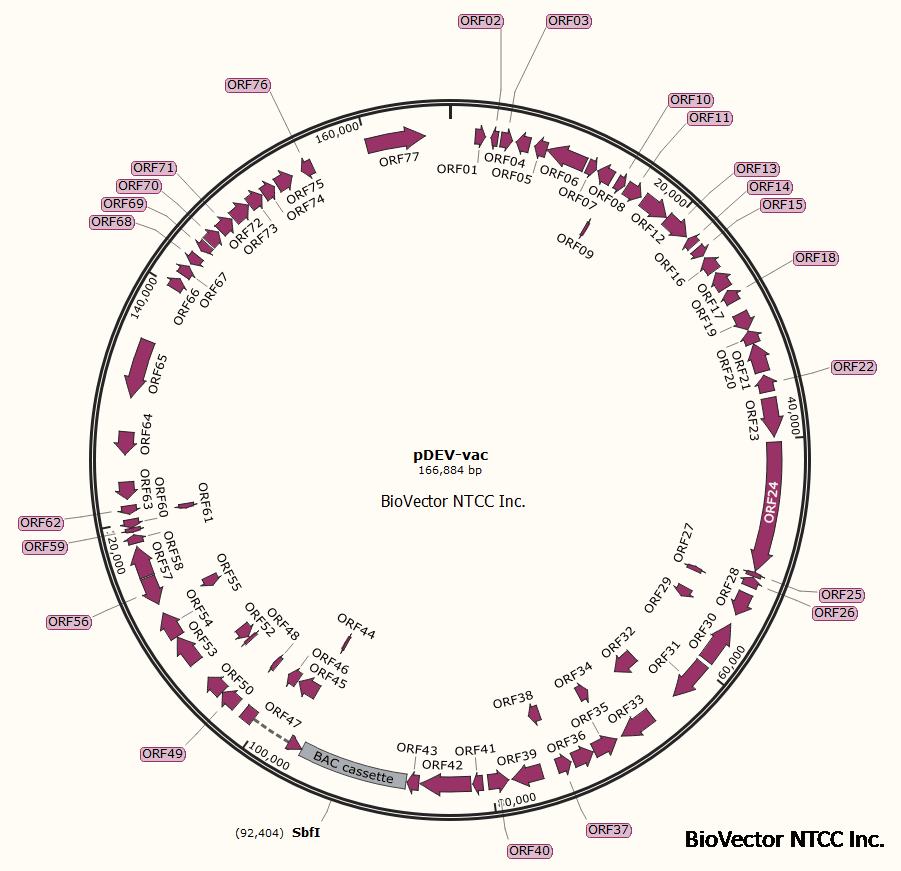
pDEV-vac
pDEV-vac鸭疫病毒疫苗株全长BAC克隆质粒
Duck enteritis virus (DEV) is the causative agent of duck viral enteritis, which causes an acute, contagious and lethal disease of many species of waterfowl within the order Anseriformes. In recent years, two laboratories have reported on the successful construction of DEV infectious clones in viral vectors to express exogenous genes. The clones obtained were either created with deletion of viral genes and based on highly virulent strains or were constructed using a traditional overlapping fosmid DNA system. Here, we report the construction of a full-length infectious clone of DEV vaccine strain that was cloned into a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC).
Methods
A mini-F vector as a BAC that allows the maintenance of large circular DNA in E. coli was introduced into the intergenic region between UL15B and UL18 of a DEV vaccine strain by homologous recombination in chicken embryoblasts (CEFs). Then, the full-length DEV clone pDEV-vac was obtained by electroporating circular viral replication intermediates containing the mini-F sequence into E. coli DH10B and identified by enzyme digestion and sequencing. The infectivity of the pDEV-vac was validated by DEV reconstitution from CEFs transfected with pDEV-vac. The reconstructed virus without mini-F vector sequence was also rescued by co-transfecting the Cre recombinase expression plasmid pCAGGS-NLS/Cre and pDEV-vac into CEF cultures. Finally, the in vitro growth properties and immunoprotection capacity in ducks of the reconstructed viruses were also determined and compared with the parental virus.
Results
The full genome of the DEV vaccine strain was successfully cloned into the BAC, and this BAC clone was infectious. The in vitro growth properties of these reconstructions were very similar to parental DEV, and ducks immunized with these viruses acquired protection against virulent DEV challenge.
Conclusions
DEV vaccine virus was cloned as an infectious bacterial artificial chromosome maintaining full-length genome without any deletions or destruction of the viral coding sequence, and the viruses rescued from the DEV-BAC clone exhibited wild-type phenotypes both in vitro and in vivo. The generated infectious clone will greatly facilitate studies on the individual genes of DEV and applications in gene deletion or live vector vaccines.
Nucleotide sequence of pDEV-vac
Map图谱:
BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞基因保藏中心
您正在向 biovector.net 发送关于产品 pDEV-vac BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞基因保藏中心 的询问
- 公告/新闻