pNZ2122乳酸菌食品级表达载体 BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞基因保藏中心
- 价 格:¥19200
- 货 号:pNZ2122乳酸菌食品级表达载体
- 产 地:北京
- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
pNZ8122乳酸菌食品级表达载体
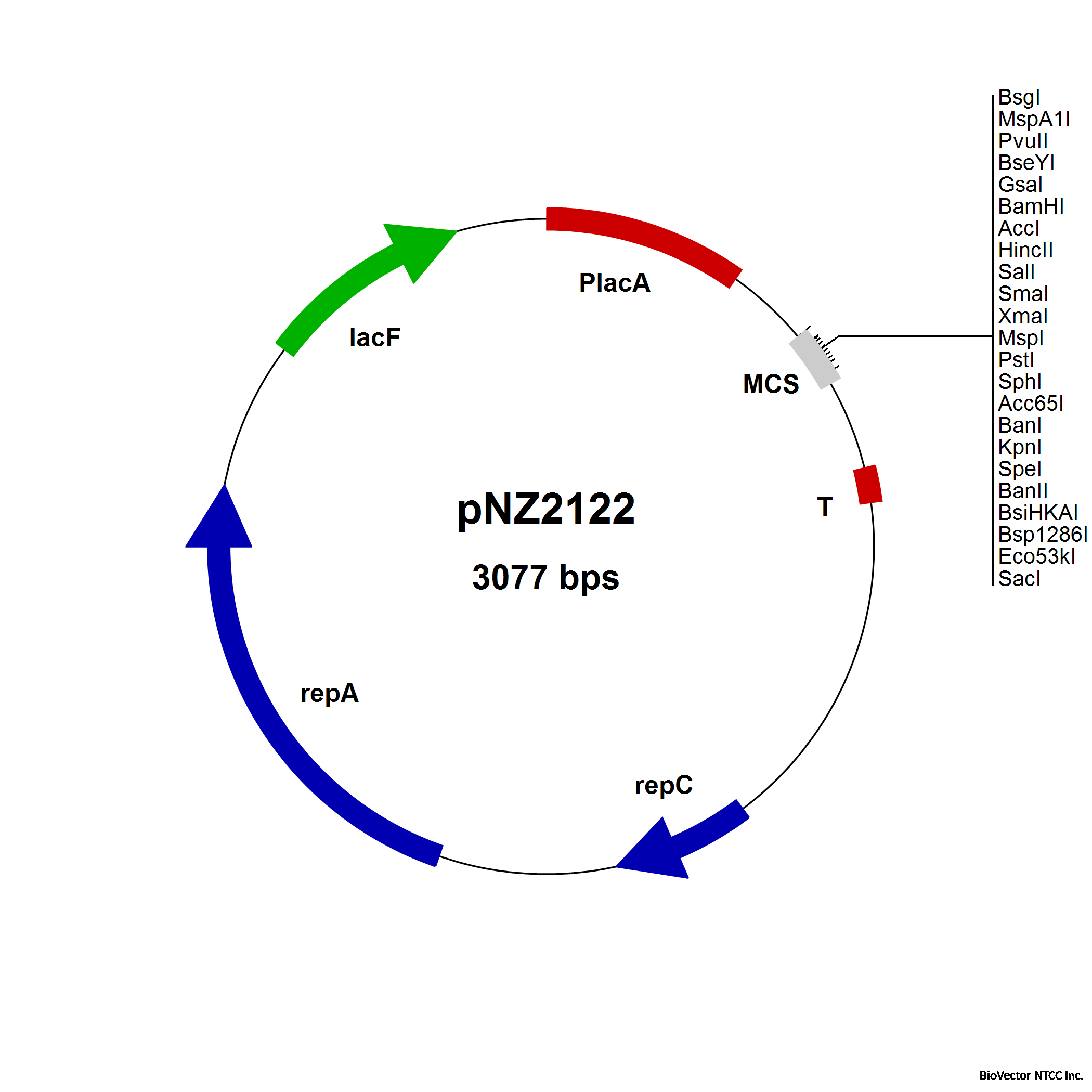
pNZ2122 plasmid
Food grade vector for constitutive gene expression under control of the lacA promoter for
L. lactis NZ3000. For transcriptional fusions. LacF-based selection. (Platteeuw et al.,1996)
Host strains
Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris MG1363
Plasmid-free progeny of the dairy strain NCDO712. Most widely used host strain for
cloning and gene expression in L. lactis (Gasson, 1983).
Lactococcus lactis NZ3000
Standard strain for food grade selection based upon the ability to grow on lactose. The
lactose operon, that is generally present on plasmids, has been integrated into the
chromosome and the lacF gene was deleted. Deletion of the lacF gene makes this strain
unable to grow on lactose unless lacF is provided on a plasmid (van Alen-Boerrigter, I. J.,
and W. M. de Vos, unpublished data; de Ruyter et al., 1996).
Strains Plasmids Medium
Lactococcus lactis MG1363 non-food grade M17 + 0.5% glucose + 10 μg/ml chloramphenicol
Lactococcus lactis NZ3000 food grade see 3.2 & 3.6
2.2 Plasmids
All plasmids are based on the pSH71 rolling circle replicon (de Vos, 1987).
pNZ124 General broad host range cloning vector with multiple cloning site for L. lactis and other
lactic acid bacteria. Chloramphenicol selection. (Platteeuw et al., 1994)
pNZ2105 General food grade cloning vector with multiple cloning site for L. lactis NZ3000. LacFbased
selection. (Platteeuw et al., 1996)
pNZ2103 Broad host range vector for constitutive gene expression under control of the lacA
promoter. For transcriptional fusion. Chloramphenicol selection. (Platteeuw et al., 1996)
pNZ7021 Broad host range vector for constitutive gene expression under control of the strong pepN
promoter. For transcriptional fusion. Chloramphenicol selection. (Wegkamp et al., 2007)
pNZ2122 Food grade vector for constitutive gene expression under control of the lacA promoter for
L. lactis NZ3000. For transcriptional fusions. LacF-based selection. (Platteeuw et al.,1996)
pNZ2123 Food grade vector. Identical to pNZ2122, but with inverted multiple cloning site (MCS).
LacF-based selection. (Platteeuw et al., 1996)
1 Introduction
The Constitutive Gene Expression System for Lactococcus lactis and Other Lactic
Acid Bacteria, developed at NIZO food research BV, The Netherlands, is easy-tooperate
and has advantages for the following applications:
Overexpression of homologous and heterologous genes for functional studies and
to obtain large quantities of specific gene products
Metabolic engineering
Suitability for protein secretion (Novotny, R. et al. 2005; Ravn, P. et al. 2003; van
Asseldonk et al., 1990; Vos, P. et al. 1989) and anchoring in the cell envelope
Large scale applications
Major advantages of this system over other expression systems are:
- Less endogenous and no exogenous proteases
- Endotoxin-free expression system
- Food grade protein expression possible
- No formation of inclusion bodies
- No formation of spores
- Simple fermentation, scale-up and downstream processing
- Suitable also for bacteria other than Lactococcus lactis
1.1 Lactococcus lactis
Lactococcus lactis is a homofermentative bacterium. Its primary function is rapid lactic
acid production from lactose. Functional characteristics that have extensively been
studied in lactococci include the carbon metabolism, the extracellular and intracellular
proteolytic system, the production of antibiotic substances, and their interaction with and
resistance to bacteriophages. The genome information of many L. lactis strains is publicly
available. This wealth of knowledge and experience has led to the use of lactococci in
several fields of biotechnology, e.g., the expression of bacterial and viral antigens for
safe vaccination via mucosal immunization, the production of human cytokines and other
therapeutic agents for in situ treatments, the use of lactococci as a cell factory for the
production of specific compounds, and the pilot production of pharmaceutical products
(Mierau, 2005).
1.2 Use of Lactococcus lactis plasmids in other Gram-positive bacteria
Plasmids with a replication origin from L. lactis can be used in all lactic acid bacteria and
in other Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis (Silke David, 1989, AEM
55:1483; Christ Platteeuw, 1994, AEM 60:587; Elisabeth Sorvig, 2005, Microbiology,
151:2439; Indranil Biswas, 2008, Microbiology, 154:2275).
1.3 Codon usage
Until very recently codon usage was an important issue in the possibility and efficiency to
express heterologous genes in L. lactis (GC content of the DNA of 35 - 37%). When a
gene donor organism is closely related to L. lactis, or the DNA GC content is similar to
that of L. lactis, the probability that a gene can successfully be expressed is high. With
the availability of cheap and reliable custom DNA synthesis, there are no longer
restrictions as to the origin of a specific target gene, since, from a known amino acid
sequence, a gene can be designed that fits the codon usage pattern of the host
organism. In addition to a general codon optimization, specific codon tables can be used,
such as the codon table for the highly expressed ribosomal protein genes, to further
increase product formation.
Map图谱:
BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞基因保藏中心
您正在向 biovector.net 发送关于产品 pNZ2122乳酸菌食品级表达载体 BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞基因保藏中心 的询问
- 公告/新闻